Leave Your Message
-
Phone
-
E-mail
-
Whatsapp
Choosing the right toughened glass for your project can be challenging. Toughened glass is known for its strength and safety features. It undergoes a heating and cooling process that makes it much stronger than standard glass. However, not all types are the same.
When selecting toughened glass, consider the specific needs of your project. The thickness and size can vary greatly. Moreover, the intended use plays a crucial role in the selection process. For example, a glass panel for a shower looks different than one for a storefront.
It’s also vital to reflect on potential imperfections. Some toughened glass may have slight defects that affect its clarity or strength. Always inspect samples carefully. Weigh the benefits and drawbacks. In the end, the right choice will enhance your project and provide durability you can rely on.
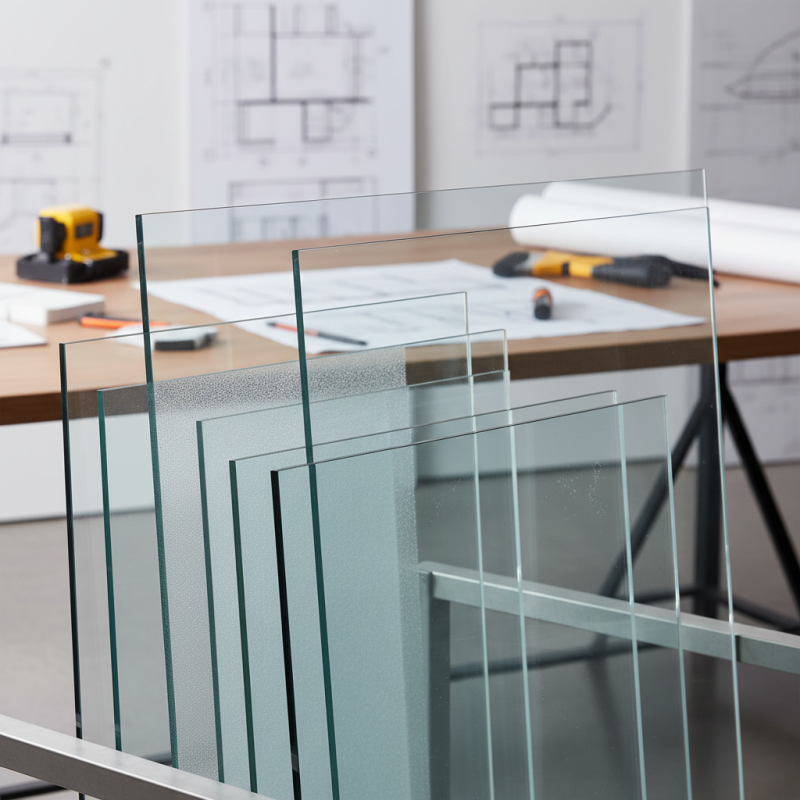

Toughened glass, also known as tempered glass, is a type of safety glass that has been treated to withstand high stress. It undergoes a heating and cooling process, making it much stronger than standard glass. According to industry data, toughened glass is able to withstand impacts up to five times stronger than standard glass. This property enhances its suitability for a range of applications, from facades to shower doors and glass furniture.
The benefits of toughened glass extend beyond just strength. It is less likely to shatter, reducing the risk of injury, and if it does break, it fractures into small, blunt pieces. Additionally, toughened glass can withstand extreme temperatures, making it ideal for environments with fluctuating heat, such as conservatories. However, not all toughened glass is created equally. The manufacturing process can vary, leading to inconsistencies in quality. This aspect often raises questions about performance in critical applications.
When choosing toughened glass, it’s essential to consider the specific needs of your project. Factors like thickness, finish, and edge treatment play a significant role in performance and aesthetics. For instance, a 6 mm thickness might suffice for a shower door, but larger panels require at least 10 mm for safety. Ignoring these details can lead to issues down the line, as miscalculations in strength could pose safety risks.
This bar chart illustrates the benefits of toughened glass across different dimensions such as safety, thermal resistance, impact resistance, weight, and cost effectiveness. Each attribute is scored on a scale from 0 to 100 to provide a visual comparison of their importance in various applications.
When selecting toughened glass, it's essential to understand the various types available. Each type serves a specific purpose, depending on the application. For instance, heat-strengthened glass is ideal for areas with high thermal stress. It's more resistant than standard glass but less strong than fully toughened options. This makes it suitable for buildings that undergo temperature fluctuations.
Another option is laminated toughened glass. This type combines layers of glass with an interlayer, providing additional safety. It's perfect for windows in high-traffic areas or places prone to breakage. You can usually see it in shopping centers or public buildings. Even with its benefits, it's vital to consider installation challenges. Proper installation can be tricky and may require trained professionals.
Tempered glass, on the other hand, is known for its strength. It's used in places like shower doors and glass facades. The process it undergoes increases durability. However, once tempered, it can't be cut. It's crucial to determine exact measurements beforehand. Weighing the pros and cons of each type can feel overwhelming but is vital for project success. Make sure to reflect on specific needs before making a choice.
When selecting toughened glass for your project, several critical factors come into play. The thickness of the glass is paramount. A typical range is 4mm to 19mm, with increased thickness offering better strength and safety. According to the Glass & Glazing Federation, thicker glasses can withstand greater impact. However, thicker options also mean more weight, which might require additional framing support.
Optical clarity is another vital consideration. Not all toughened glass is created equal in terms of transparency. Lower quality options can distort colors and images. Studies show that high-quality toughened glass maintains a light transmission of over 90%. This is essential for spaces designed to maximize natural light.
You must also address thermal performance. Some toughened glass options are treated for better insulation. The Energy Saving Trust states that using energy-efficient glass can reduce heating costs by up to 50%. Think about your project's climate and intended use before making a selection. Sometimes, overlooking these details can lead to dissatisfaction later. Prioritizing specific characteristics will depend on your unique needs and preferences.
Toughened glass is widely used in construction and design due to its strength and safety features. According to a report from the Glass Association, toughened glass can withstand temperatures up to 300°C and is five to seven times stronger than regular glass. In high-rise buildings, it serves as a crucial element in facades, providing both aesthetics and durability.
In interior design, toughened glass is often used in partitions, shower doors, and tabletops. Its sleek appearance enhances modern spaces while ensuring safety. A case study from the International Journal of Architecture highlights that using toughened glass in buildings can reduce the risk of injury by 70%. Yet, it is important to consider potential drawbacks. Installation mistakes can lead to breakage, and not all projects require this high level of durability.
Besides aesthetic considerations, energy efficiency is also vital. Toughened glass can minimize energy loss when combined with insulating properties. However, some may overlook the need for proper insulation. A lack of awareness can lead to increased energy costs. Selecting the right type depends on specific project needs and the environment in which it will be used. Understanding these aspects can lead to better design outcomes.
| Application Area | Type of Toughened Glass | Benefits | Thickness Options (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Building Facades | Tempered Glass | High strength, thermal resistance | 6 - 19 |
| Shower Enclosures | Laminated Toughened Glass | Safety, sound insulation | 10 - 12 |
| Glass Doors | Heat Strengthened Glass | Impact resistance, less risk of breakage | 8 - 12 |
| Balustrades | Tempered Glass | Durability, aesthetic appeal | 10 - 15 |
| Skylights | Double Glazed Toughened Glass | Energy efficiency, UV protection | 8 - 24 |

When choosing toughened glass, understanding safety standards is crucial. Toughened glass must meet strict regulations. These regulations ensure durability and protection. They are often set by industry bodies. Compliance with these standards ensures that the glass can withstand various stresses.
One key standard is the EN 12150. This European standard focuses on performance requirements. It evaluates aspects like thermal stress resistance and impact strength. Projects using toughened glass should always reference these standards. Failure to do so can lead to safety hazards.
Additionally, local regulations may also apply. It’s essential to verify these requirements before purchasing. Each project might have different specifications. Without proper adherence to standards, the integrity of the installation could be compromised. Consider consulting professionals who understand the regulations well. Their insights can help avoid costly mistakes. Ultimately, safety and quality should be your top priority.